The technical standard in SEPA
SEPA payments are processed on the basis of the respective current versions of the European Payments Council documentation (Rulebooks and Implementation Guidelines).
The European banking industry developed the SEPA payment instruments as XML message formats based on the global ISO 20022 standard. In future, this uniform technical standard will form the basis for the interoperability of payment service providers and payment infrastructures and enables a fully automated settlement of payments in the SEPA area.
In a significant departure from the previous domestic procedures, the payer and the payee (as well as their payment service providers) are to be identified by IBAN and BIC, and not by the domestic bank sort code and account number.
IBAN
IBAN is short for International Bank Account Number, and is a standardised International bank/account number for domestic and cross-border payments. It consists of a maximum of 34 digits, which can be used differently depending on the country. Only the first four digits are fixed.
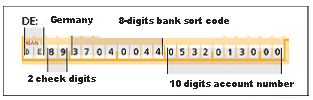
Bank customers can find their IBAN on their bank statements. The German banking industry has various automated solutions in place for changing the account data relating to account numbers and bank sort codes in use today in German payment transactions into the internationally used IBAN and BIC, eg the internet-based IBAN conversion service (available in German only).
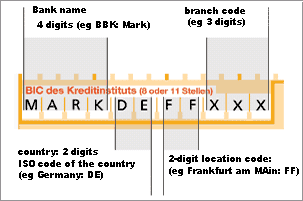
BIC
The BIC (Bank Identifier Code) is a payment service provider's international bank sort code. It consists of a maximum of 11 digits, and is often called the SWIFT code.